Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services — from applications to storage and processing power — typically over the internet and on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Rather than owning their own computing infrastructure or data centers, companies can rent access to anything from applications to storage from a cloud service provider.
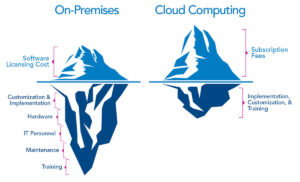
One benefit of using cloud computing services is that firms can avoid the upfront cost and complexity of owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure, and instead simply pay for what they use, when they use it.
In turn, providers of cloud computing services can benefit from significant economies of scale by delivering the same services to a wide range of customers.
What Cloud Computing Services are Available?
Cloud computing services cover a vast range of options now, from the basics of storage, networking, and processing power through to natural language processing and artificial intelligence as well as standard office applications. Pretty much any service that doesn’t require you to be physically close to the computer hardware that you are using can now be delivered via the cloud.
Examples of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing underpins a vast number of services. That includes consumer services like Gmail or the cloud back-up of the photos on your smartphone, though to the services which allow large enterprises to host all their data and run all of their applications in the cloud. Netflix relies on cloud computing services to run its video streaming service and its other business systems too, and have a number of other organisations.
Cloud computing is becoming the default option for many apps: software vendors are increasingly offering their applications as services over the internet rather than standalone products as they try to switch to a subscription model. However, there is a potential downside to cloud computing, in that it can also introduce new costs and new risks for companies using it.
Why Is It Called Cloud Computing?
A fundamental concept behind cloud computing is that the location of the service, and many of the details such as the hardware or operating system on which it is running, are largely irrelevant to the user. It’s with this in mind that the metaphor of the cloud was borrowed from old telecoms network schematics, in which the public telephone network (and later the internet) was often represented as a cloud to denote that the underlying technologies were irrelevant.
What Is the History of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing as a term has been around since the early 2000s, but the concept of computing-as-a-service has been around for much, much longer — as far back as the 1960s, when computer bureaus would allow companies to rent time on a mainframe, rather than have to buy one themselves.
These ‘time-sharing’ services were largely overtaken by the rise of the PC which made owning a computer much more affordable, and then by the rise of corporate data centers where companies would store vast amounts of data.
But the concept of renting access to computing power has resurfaced a number of times since then — in the application service providers, utility computing, and grid computing of the late 1990s and early 2000s.
This was followed by cloud computing, which really took hold with the emergence of software as a service and hyperscale cloud computing providers such as Amazon Web Services.
Cloud Computing Benefits
The exact benefits will vary according to the type of cloud service being used but, fundamentally, using cloud services means companies not having to buy or maintain their own computing infrastructure.
No more buying servers, updating applications or operating systems, or decommissioning and disposing of hardware or software when it is out of date, as it is all taken care of by the supplier. For commodity applications, such as email, it can make sense to switch to a cloud provider, rather than rely on in-house skills. A company that specializes in running and securing these services is likely to have better skills and more experienced staff than a small business could afford to hire, so cloud services may be able to deliver a more secure and efficient service to end users.
Using cloud services means companies can move faster on projects and test out concepts without lengthy procurement and big upfront costs, because firms only pay for the resources they consume. This concept of business agility is often mentioned by cloud advocates as a key benefit. The ability to spin up new services without the time and effort associated with traditional IT procurement should mean that is easier to get going with new applications faster. And if a new application turns out to be a wildly popular the elastic nature of the cloud means it is easier to scale it up fast.
Source: ZDNET